When can you profitably go all-in with a hand? Which hands can you call an all-in with? Answers to these questions are provided by pushbot charts and equilibrium strategies. This article will provide equilibrium push bot charts for poker tournaments and explain how and when to use them.
Preflop Charts FAQ Where is the chart for the Big Blind? These are Raise First In charts, meaning you raise with these hands when the action folds around to you. When the action folds around to you in the Big Blind, the hand is over and you win the pot. If I choose which hands to play based on these charts, won’t that make me predictable? Take a Push Fold Chart Home With You! Now you can carry our unexploitable, Push/Fold charts with you anywhere you go for only $3.95. All the charts for a full game are included in this handy, pocket-sized, glossy card that allows you to play perfect poker any time you get below ten big blinds. Using Preflop Range Charts. The bottom line is that there will be preflop situations in your poker career where you will deviate from these ranges, but tread carefully. Use our free fold equity calculator before you shove your next flush draw to make sure your play is +EV. Enter poker range charts. These handy tools allow players to see which poker hand ranges to play in preflop scenarios where the pot is unopened and a player plans to shove or fold.
Example situation in a tournament
Let’s say we’re in the late stages of a big tournament. The stacks are shallow and most action happens before the flop. We’re in the small blind with a mediocre holding (say K6) and a small stack (say 9 big blinds). It is folded to us. What do we do?
Or, let’s say we’re in the big blind with the same hand and the same stack. Everybody folds to the small blind – a good and aggressive player – and he goes all-in. What do we do now?
Pushbot charts help making decisions in situations like the ones in this example. In this article we’re going to focus on equilibrium pushbot charts which work for push-or-fold decisions between the small blind and the big blind and to some extend between the button and the blinds.
Equilibrium pushbot and callbot charts
The tables below show the maximum effective stack for a profitable push from the small blind against the big blind and the maximum effective stack for a profitable call from the big big blind according to equilibrium strategies. (The effective stack is the smaller of the stack sizes between you and your opponent.)
Equilibrium pushbot chart for moving all-in from the small-blind
| Suited Cards | |||||||||||||
| O f f s u i t C a r d s | AA50 | AKs50 | AQs50 | AJs50 | ATs50 | A9s50 | A8s50 | A7s50 | A6s50 | A5s50 | A4s50 | A3s50 | A2s48 |
| AKo50 | KK50 | KQs50 | KJs50 | KTs50 | K9s50 | K8s50 | K7s49 | K6s36 | K5s32 | K4s26 | K3s20 | K2s19 | |
| AQo50 | KQo50 | QQ50 | QJs50 | QTs50 | Q9s50 | Q8s50 | Q7s20 | Q6s29 | Q5s24 | Q4s16 | Q3s14 | Q2s13 | |
| AJo50 | KJo50 | QJo50 | JJ50 | JTs50 | J9s50 | J8s50 | J7s32 | J6s19 | J5s16 | J4s14 | J3s11 | J2s8.8 | |
| ATo50 | KTo50 | QTo45 | JTo46 | TT50 | T9s50 | T8s50 | T7s36 | T6s25 | T5s12 | T4s11 | T3s7.7 | T2s6.5 | |
| A9o45 | K9o24 | Q9o24 | J9o29 | T9o32 | 9950 | 98s50 | 97s36 | 96s27 | 95s14 | 94s6.9 | 93s4.9 | 92s3.7 | |
| A8o43 | K8o19 | Q8o13 | J8o14 | T8o18 | 98o21 | 8850 | 87s43 | 86s31 | 85s19 | 84s10 | 83s2.7 | 82s2.5 | |
| A7o41 | K7o16 | Q7o10 | J7o8.5 | T7o9.9 | 97o11 | 87o16 | 7750 | 76s36 | 75s24 | 74s14 | 73s2.5 | 72s2.1 | |
| A6o35 | K6o15 | Q6o9.8 | J6o6.5 | T6o5.7 | 96o5.2 | 86o7.1 | 76o11 | 6650 | 65s29 | 64s16 | 63s7.1 | 62s2 | |
| A5o37 | K5o14 | Q5o8.9 | J5o6 | T5o4.1 | 95o3.5 | 85o3 | 75o2.6 | 65o2.4 | 5550 | 54s24 | 53s13 | 52s2 | |
| A4o35 | K4o13 | Q4o8.3 | J4o5.4 | T4o3.8 | 94o2.7 | 84o2.3 | 74o2.1 | 64o2 | 54o2.1 | 4450 | 43s10 | 42s1.8 | |
| A3o32 | K3o13 | Q3o7.5 | J3o5 | T3o3.4 | 93o2.5 | 83o1.9 | 73o1.8 | 63o1.7 | 53o1.8 | 43o1.6 | 3350 | 32s1.7 | |
| A2o29 | K2o12 | Q2o7 | J2o4.6 | T2o3 | 92o2.2 | 82o1.8 | 72o1.6 | 62o1.5 | 52o1.5 | 42o1.4 | 32o1.4 | 2250 | |
You can shove all-in profitably:
- If you are in the small blind,
- everyone before you has folded,
- your effective stack (in big blinds) is smaller than the number given in this table.
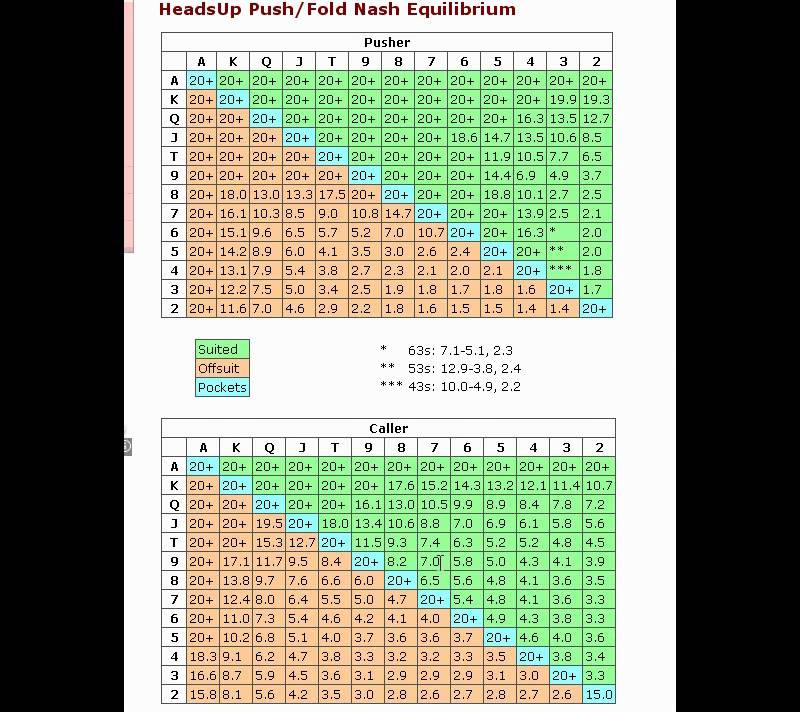
Note: the maximum stack size considered is 50 big blinds.
Download this chart as PDF
Calculations by Bill Chen and Jerrod Ankenman (Mathematics of Poker)
Equilibrium callbot chart for calling an all-in in the big blind
| Suited Cards | |||||||||||||
| O f f s u i t C a r d s | AA50 | AKs50 | AQs50 | AJs50 | ATs50 | A9s47 | A8s41 | A7s36 | A6s31 | A5s30 | A4s26 | A3s25 | A2s23 |
| AKo50 | KK50 | KQs50 | KJs45 | KTs32 | K9s24 | K8s18 | K7s15 | K6s14 | K5s13 | K4s12 | K3s11 | K2s11 | |
| AQo50 | KQo46 | QQ50 | QJs29 | QTs24 | Q9s16 | Q8s13 | Q7s11 | Q6s10 | Q5s8.9 | Q4s8.5 | Q3s7.8 | Q2s7.2 | |
| AJo50 | KJo27 | QJo20 | JJ50 | JTs18 | J9s14 | J8s11 | J7s8.8 | J6s7.1 | J5s6.9 | J4s6.2 | J3s5.8 | J2s5.6 | |
| ATo50 | KTo24 | QTo16 | JTo13 | TT50 | T9s12 | T8s9.3 | T7s7.4 | T6s6.3 | T5s5.2 | T4s5.2 | T3s4.8 | T2s4.5 | |
| A9o40 | K9o18 | Q9o12 | J9o9.9 | T9o8.5 | 9950 | 98s8.3 | 97s7 | 96s5.8 | 95s5 | 94s4.3 | 93s4.1 | 92s3.9 | |
| A8o35 | K8o14 | Q8o9.8 | J8o7.7 | T8o6.7 | 98o6.1 | 8850 | 87s6.5 | 86s5.6 | 85s4.8 | 84s4.1 | 83s3.6 | 82s3.5 | |
| A7o29 | K7o13 | Q7o8 | J7o6.4 | T7o5.5 | 97o5 | 87o4.7 | 7750 | 76s5.4 | 75s4.8 | 74s4.1 | 73s3.6 | 72s3.3 | |
| A6o22 | K6o11 | Q6o7.4 | J6o5.4 | T6o4.7 | 96o4.2 | 86o4.1 | 76o4 | 6650 | 65s4.9 | 64s4.3 | 63s3.8 | 62s3.3 | |
| A5o21 | K5o10 | Q5o6.8 | J5o5.1 | T5o4 | 95o3.7 | 85o3.6 | 75o3.6 | 65o3.7 | 5543 | 54s4.6 | 53s4 | 52s3.6 | |
| A4o19 | K4o9.2 | Q4o6.3 | J4o4.8 | T4o3.8 | 94o3.3 | 84o3.2 | 74o3.2 | 64o3.3 | 54o3.5 | 4432 | 43s3.8 | 42s3.4 | |
| A3o17 | K3o8.8 | Q3o5.9 | J3o4.5 | T3o3.6 | 93o3.1 | 83o2.9 | 73o2.9 | 63o3 | 53o3.1 | 43o3 | 3322 | 32s3.3 | |
| A2o16 | K2o8.3 | Q2o5.6 | J2o4.2 | T2o3.5 | 92o3 | 82o2.8 | 72o2.6 | 62o2.7 | 52o2.8 | 42o2.7 | 32o2.6 | 2215 | |
You can call the all-in profitably:
- If you are in the big blind,
- everyone before the small blind has folded,
- the small blind moved all-in,
- your effective stack (in big blinds) is smaller than the number given in this table.
Note: the maximum stack size considered is 50 big blinds.
Download this chart as PDF
Calculations by Bill Chen and Jerrod Ankenman (Mathematics of Poker)
How to use these equilibrium charts?
Let’s go back to the example situations above. We’re in the small blind with K6 and a 9 big blind stack. It is folded to us. What do we do?
Checking the first table reveals that K-6-offsuit has an equilibrium push rating of 15 big blinds. Meaning, as long as our stack is 15 big blinds or smaller we can profitably move all-in.
In the second scenario we’re in the big blind with the same hand and the small blind moves all-in. Now we just check the second table and see that K-6-offsuit has an equilibrium call rating of 11 big blinds. Meaning, as long as our stack is 11 big blinds or smaller we can profitably call against the small blinds all-in.
What the hell are “equilibrium pushbot strategies”?
[su-custom_gallery source=”media: 1205″ link=”lightbox” width=”350″ height=”500″ title=”always” class=”alignright”]
No let’s examine how those pushbot and callbot charts above are derived.
Imagine a very simple Texas Hold’em game. Two players play heads-up, the small blind can decide before the flop whether to push or fold. If he pushes, the big blind can now decide whether to call or not. There are no post-flop decisions. Situations like this occur often in later stages of poker tournaments when the stack sizes are small and everybody folds to the blinds.
This simple push-or-fold game can be solved mathematically and optimal strategies can be given for both players. The optimal strategies form a balance for both players (an equilibrium). This means that none of the players can unilaterally improve their strategy.
Determining these strategies is a bit time-consuming and works (in a nutshell) like this: For each possible effective stack size, you check the range with which the small blind can profitably push if the big blind would always call. Then you check with which range the big blind can call profitably against the small blinds range. Now check again which range the small blind can push with, if the big blind only calls with the range found in the previous step. Repeat this until the ranges do not change anymore and then you have found the equilibrium strategies for the given stack size.
This way you can check for all stack sizes which hands can be pushed profitably and which hands can call an all-in profitably. Bill Chen and Jerrod Ankenman did this in the book Mathematics of Poker. The results of these calculations are charts above.
How to work with the equilibrium pushbot charts?
For each hand, the charts show the maximum stack size (in big blinds) for profitable pushes and calls according to the equilibrium strategy. The pushbot chart applies when you’re in the small blind and it is folded to you, the callbot chart applies when you’re in the big blind and the small blind open shoves.
For example, if you have J2 in the small blind, you can go all-in with an effective stack of 4.6 big blinds or less profitably. Or if you have T9 in the big blind and the small blind open shoves, you can call profitably with an effective stack of 12 big blinds or less.

Equilibrium pushbot charts from the button
The Equilibrium pushbot chart can also be used from the button. The rough approximation is as follows:
Equilibrium pushbot chart button rule
Push Shove Poker Charts
You can go all-in profitably from the button if your stack is smaller than half the equilibrium pushbot ranking for the hand you are holding.
There is no button rule for calls against a button shove in the big blind.
When can you apply equilibrium strategies profitably?
You should not start pushing your stack from the small blind just because your hand has an equilibrium pushbot ranking of 36 big blinds and you also should not blindly defend your big blind just because your stack is slightly below the equilibrium callbot ranking. The charts above give you a rough idea, which hands you can safely push with and which hands you can safely call an all-in with if your opponent is a good and aggressive player.
Conditions for the equilibrium push-fold-charts
- Late preflop position: The equilibrium pushbot chart only works from the small blind (and to a lesser extend from the button).
- Or Big Blind: The equilibrium callbot chart only works if you’re in the big blind.
- No other players: Both charts assume all other players have folded.
- No Antes: Calculations for the charts assume no antes. With antes the maximum stack size for profitable calls and pushes increases considerably.
- No ICM: No tournament specific mechanisms are considered for those charts. “Profitable” throughout this article means profitable when looking at chip-EV. In many tournament situations you have to call much tighter and can push much looser than the charts indicate.
- Skilled opponent: The charts assume your opponents are skilled, aggressive players that will call or shove with reasonable ranges. If the tightest player at the table shoves into you from the small blind, you better don’t call with K9 and a 20 big blind stack, just because the equilibrium chart says so. You fold because his range is much more narrow than any equilibrium strategy suggests.
Like the Sklansky Chubukov rankings, the equilibrium rankings help you to develop an idea which hands are good enough to merit an all-in and which hands are good enough to call an all-in against an aggressive opponent.
How do equilibrium rankings and Sklansky Chubukov rankings differ?
Another approach to explore profitable shoving ranges are the Sklansky Chubukov rankings.
While the Equilibrium strategy assumes your opponent has a realistic calling (or pushing) range, the Sklansky Chubukov strategy always assumes the worst case, namely that the opponent always calls when he has a better hand than you (or at least gets sufficient odds).

Meaning, you can push much looser using the equilibrium strategy, since this strategy takes into account that the opponent also folds some better hands. Suited connectors in particular gain significant value when using the equilibrium strategy: They have a good equity against the typical calling (and also pushing) range, which is why they are comparatively strong hands. Take 65 for example. The hand has a Sklansky Chubukov ranking of only 3.1, meaning you can only push with 3.1 or fewer big blinds. But according to the Equilibrium strategy you can push profitably with up to 29 big blinds – a huge difference.
Relevant Resources
- Sklansky Chubukov rankings
- Pushbot trainer
- Equilibrium charts with ante (HoldemResources.net)
- Nash equilibrium in poker explained (poker VIP)
- Mathematics of Poker (Amazon)
Categorised in: News
Developed by professional poker player Max Silver, SnapShove combines unexploitable nash equilibrium ranges with an instant, easy to use and flexible interface allowing you to get the perfect play for any shove, call or reshove situation.
Fold Shove Chart
SnapShove’s exclusive training mode quickly puts your short stack skills to the test with the added pressure of time. These quick reflex shove, fold and call decisions are one of the best ways to massively improve your skills rapidly over time.
Poker Shove Chart
SnapShove is used by over 54,000 poker players worldwide including many of the worlds best. Our frequent users include WSOP Bracelet winners, Super High Roller champions and many of the world’s top 300 GPI Players.
Poker Shove Range Chart Sheet
SnapShove is available FREE with a limited number of searches per day. SnapShove pro adds unlimited searches and expert features. These include instant search and the unique “SnapShove/SnapFold” buttons letting find the perfect ranges for the next hand with a single click.